Predictors of Health Care Practitioners’ Intention to Use AI-Enabled Clinical Decision Support Systems: Meta-Analysis Based on the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology
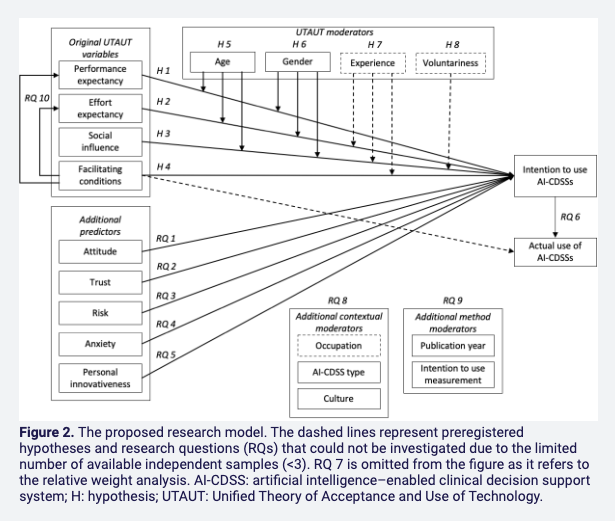
Artificial intelligence–enabled clinical decision support systems (AI-CDSSs) offer potential for improving health care outcomes, but their adoption among health care practitioners remains limited. The meta-analysis identified predictors influencing health care practitioners’ intention to use AI-CDSSs based on the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT). Additional predictors were examined based on existing empirical evidence.



